5. Kaleidoscope:擴展語言:控制流程¶
5.1. 第 5 章 簡介¶
歡迎來到“使用 LLVM 實作語言”教學的第 5 章。第 1-4 部分描述了簡單的 Kaleidoscope 語言的實作,包括支援產生 LLVM IR,接著是最佳化和 JIT 編譯器。不幸的是,就目前呈現的 Kaleidoscope 而言,它幾乎沒有用處:除了呼叫和返回之外,它沒有任何控制流程。這表示您無法在程式碼中加入條件分支,這大大限制了它的功能。在本集“建構編譯器”中,我們將擴展 Kaleidoscope,使其具有 if/then/else 表達式和一個簡單的 ‘for’ 迴圈。
5.2. If/Then/Else(如果/那麼/否則)¶
擴展 Kaleidoscope 以支援 if/then/else 非常簡單。它基本上需要將對這個“新”概念的支援添加到詞法分析器、剖析器、抽象語法樹和 LLVM 程式碼發射器中。這個範例很好,因為它展示了隨著時間的推移“成長”一種語言是多麼容易,隨著新想法的發現而逐步擴展它。
在我們開始討論“如何”添加這個擴展之前,讓我們先談談我們“想要什麼”。基本概念是我們希望能夠編寫這樣的東西
def fib(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
fib(x-1)+fib(x-2);
在 Kaleidoscope 中,每個建構都是一個表達式:沒有陳述句。因此,if/then/else 表達式需要像任何其他表達式一樣返回一個值。由於我們主要使用函數式形式,我們將讓它評估其條件,然後根據條件的解析方式返回 ‘then’ 或 ‘else’ 值。這與 C 的 “?:” 表達式非常相似。
if/then/else 表達式的語義是將條件評估為布林相等值:0.0 被視為 false,其他任何值都被視為 true。如果條件為 true,則評估並返回第一個子表達式;如果條件為 false,則評估並返回第二個子表達式。由於 Kaleidoscope 允許副作用,因此這種行為對於確定下來非常重要。
現在我們知道我們“想要”什麼,讓我們將其分解為組成部分。
5.2.1. If/Then/Else 的詞法分析器擴展¶
詞法分析器擴展很簡單。首先,我們為相關的 token 添加新的列舉值
// control
tok_if = -6,
tok_then = -7,
tok_else = -8,
一旦我們有了這些,我們就可以在詞法分析器中識別新的關鍵字。這非常簡單
...
if (IdentifierStr == "def")
return tok_def;
if (IdentifierStr == "extern")
return tok_extern;
if (IdentifierStr == "if")
return tok_if;
if (IdentifierStr == "then")
return tok_then;
if (IdentifierStr == "else")
return tok_else;
return tok_identifier;
5.2.2. If/Then/Else 的抽象語法樹擴展¶
為了表示新的表達式,我們為其添加一個新的抽象語法樹節點
/// IfExprAST - Expression class for if/then/else.
class IfExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Cond, Then, Else;
public:
IfExprAST(std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Cond, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Then,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Else)
: Cond(std::move(Cond)), Then(std::move(Then)), Else(std::move(Else)) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
抽象語法樹節點僅包含指向各種子表達式的指標。
5.2.3. If/Then/Else 的剖析器擴展¶
現在我們有了來自詞法分析器的相關 token,並且我們有了要建構的抽象語法樹節點,我們的剖析邏輯相對簡單。首先,我們定義一個新的剖析函數
/// ifexpr ::= 'if' expression 'then' expression 'else' expression
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseIfExpr() {
getNextToken(); // eat the if.
// condition.
auto Cond = ParseExpression();
if (!Cond)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != tok_then)
return LogError("expected then");
getNextToken(); // eat the then
auto Then = ParseExpression();
if (!Then)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != tok_else)
return LogError("expected else");
getNextToken();
auto Else = ParseExpression();
if (!Else)
return nullptr;
return std::make_unique<IfExprAST>(std::move(Cond), std::move(Then),
std::move(Else));
}
接下來,我們將其連接為主要表達式
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (CurTok) {
default:
return LogError("unknown token when expecting an expression");
case tok_identifier:
return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case tok_number:
return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(':
return ParseParenExpr();
case tok_if:
return ParseIfExpr();
}
}
5.2.4. If/Then/Else 的 LLVM IR¶
現在我們已經完成了剖析和建構抽象語法樹,最後一步是添加 LLVM 程式碼產生支援。這是 if/then/else 範例中最有趣的部分,因為這是它開始引入新概念的地方。以上所有程式碼都在之前的章節中進行了詳盡的描述。
為了激勵我們想要產生的程式碼,讓我們看一下一個簡單的範例。考慮
extern foo();
extern bar();
def baz(x) if x then foo() else bar();
如果您停用最佳化,您將(很快)從 Kaleidoscope 獲得的程式碼如下所示
declare double @foo()
declare double @bar()
define double @baz(double %x) {
entry:
%ifcond = fcmp one double %x, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %ifcond, label %then, label %else
then: ; preds = %entry
%calltmp = call double @foo()
br label %ifcont
else: ; preds = %entry
%calltmp1 = call double @bar()
br label %ifcont
ifcont: ; preds = %else, %then
%iftmp = phi double [ %calltmp, %then ], [ %calltmp1, %else ]
ret double %iftmp
}
為了視覺化控制流程圖,您可以使用 LLVM ‘opt’ 工具的一個漂亮功能。如果您將此 LLVM IR 放入 “t.ll” 並執行 “llvm-as < t.ll | opt -passes=view-cfg”,將會彈出一個視窗,您將看到此圖表
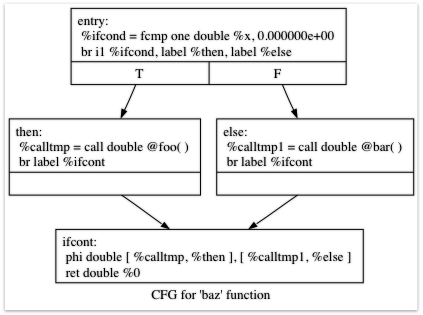
圖 5.1 範例 CFG¶
另一種取得此圖表的方法是呼叫 “F->viewCFG()” 或 “F->viewCFGOnly()”(其中 F 是 “Function*”),方法是將實際呼叫插入程式碼中並重新編譯,或在偵錯器中呼叫這些呼叫。LLVM 有許多用於視覺化各種圖表的美好功能。
回到產生的程式碼,它相當簡單:entry 區塊評估條件表達式(在本例中為 “x”),並使用 “fcmp one” 指令(‘one’ 是 “Ordered and Not Equal”(已排序且不相等))將結果與 0.0 進行比較。根據此表達式的結果,程式碼會跳轉到 “then” 或 “else” 區塊,其中包含 true/false 情況的表達式。
一旦 then/else 區塊執行完成,它們都會分支返回到 ‘ifcont’ 區塊,以執行 if/then/else 之後發生的程式碼。在本例中,剩下的唯一事情是返回到函數的呼叫者。然後問題變成:程式碼如何知道要返回哪個表達式?
這個問題的答案涉及一個重要的 SSA 操作:Phi 操作。如果您不熟悉 SSA,維基百科文章是一個很好的介紹,並且在您最喜歡的搜尋引擎上還有各種其他介紹。簡短的版本是,Phi 操作的 “執行” 需要 “記住” 控制來自哪個區塊。Phi 操作採用與輸入控制區塊對應的值。在本例中,如果控制來自 “then” 區塊,它會取得 “calltmp” 的值。如果控制來自 “else” 區塊,它會取得 “calltmp1” 的值。
此時,您可能開始想 “糟糕!這表示我簡單而優雅的前端將必須開始產生 SSA 形式才能使用 LLVM!”。幸運的是,情況並非如此,我們強烈建議不要在您的前端實作 SSA 建構演算法,除非有非常好的理由這樣做。實際上,在為您的平均命令式程式設計語言編寫的程式碼中,有兩種值可能會需要 Phi 節點
涉及使用者變數的程式碼:
x = 1; x = x + 1;AST 結構中隱含的值,例如本例中的 Phi 節點。
在本教學的第 7 章(“可變變數”)中,我們將深入討論 #1。現在,請相信我,您不需要 SSA 建構來處理這種情況。對於 #2,您可以選擇使用我們將為 #1 描述的技術,或者您可以直接插入 Phi 節點(如果方便的話)。在本例中,產生 Phi 節點非常容易,因此我們選擇直接執行。
好的,關於動機和概述就夠了,讓我們產生程式碼吧!
5.2.5. If/Then/Else 的程式碼產生¶
為了為此產生程式碼,我們為 IfExprAST 實作 codegen 方法
Value *IfExprAST::codegen() {
Value *CondV = Cond->codegen();
if (!CondV)
return nullptr;
// Convert condition to a bool by comparing non-equal to 0.0.
CondV = Builder->CreateFCmpONE(
CondV, ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(0.0)), "ifcond");
此程式碼很簡單,與我們之前看到的類似。我們發射條件的表達式,然後將該值與零進行比較,以獲得作為 1 位元(布林值)值的真值。
Function *TheFunction = Builder->GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
// Create blocks for the then and else cases. Insert the 'then' block at the
// end of the function.
BasicBlock *ThenBB =
BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "then", TheFunction);
BasicBlock *ElseBB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "else");
BasicBlock *MergeBB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "ifcont");
Builder->CreateCondBr(CondV, ThenBB, ElseBB);
此程式碼會建立與 if/then/else 陳述句相關的基本區塊,並直接對應於上述範例中的區塊。第一行取得正在建構的目前 Function 物件。它透過詢問建構器目前的 BasicBlock,並詢問該區塊的 “父項”(它目前嵌入到的函數)來取得它。
一旦它有了該物件,它就會建立三個區塊。請注意,它將 “TheFunction” 傳遞到 “then” 區塊的建構函式中。這會導致建構函式自動將新區塊插入到指定函數的末尾。建立其他兩個區塊,但尚未插入到函數中。
建立區塊後,我們可以發射在它們之間進行選擇的條件分支。請注意,建立新區塊不會隱式影響 IRBuilder,因此它仍然插入到條件進入的區塊中。另請注意,它正在建立到 “then” 區塊和 “else” 區塊的分支,即使 “else” 區塊尚未插入到函數中。這一切都沒問題:這是 LLVM 支援向前參考的標準方式。
// Emit then value.
Builder->SetInsertPoint(ThenBB);
Value *ThenV = Then->codegen();
if (!ThenV)
return nullptr;
Builder->CreateBr(MergeBB);
// Codegen of 'Then' can change the current block, update ThenBB for the PHI.
ThenBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
在插入條件分支後,我們移動建構器以開始插入到 “then” 區塊中。嚴格來說,此呼叫將插入點移動到位於指定區塊的末尾。但是,由於 “then” 區塊是空的,因此它也從區塊的開頭開始插入。:)
設定插入點後,我們從 AST 遞迴地產生 “then” 表達式的程式碼。為了完成 “then” 區塊,我們建立一個到 merge 區塊的無條件分支。LLVM IR 的一個有趣(且非常重要)的方面是,它要求所有基本區塊都必須以 控制流程指令(例如 return 或 branch)“終止”。這表示所有控制流程(包括 fall throughs)都必須在 LLVM IR 中明確表示。如果您違反此規則,驗證器將發出錯誤。
此處的最後一行非常微妙,但非常重要。基本問題是,當我們在 merge 區塊中建立 Phi 節點時,我們需要設定區塊/值對,以指示 Phi 的工作方式。重要的是,Phi 節點期望為 CFG 中區塊的每個前導節點都有一個條目。那麼,為什麼當我們在上面 5 行將其設定為 ThenBB 時,我們還要取得目前的區塊?問題是,如果 “Then” 表達式本身包含巢狀 “if/then/else” 表達式,則它實際上可能會變更建構器正在發射程式碼的區塊。由於遞迴呼叫 codegen() 可能會任意變更目前區塊的概念,因此我們需要取得最新的值,以用於設定 Phi 節點的程式碼。
// Emit else block.
TheFunction->insert(TheFunction->end(), ElseBB);
Builder->SetInsertPoint(ElseBB);
Value *ElseV = Else->codegen();
if (!ElseV)
return nullptr;
Builder->CreateBr(MergeBB);
// codegen of 'Else' can change the current block, update ElseBB for the PHI.
ElseBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
‘else’ 區塊的程式碼產生基本上與 ‘then’ 區塊的程式碼產生相同。唯一顯著的差異是第一行,它將 ‘else’ 區塊添加到函數中。回想一下,先前建立了 ‘else’ 區塊,但未將其添加到函數中。現在 ‘then’ 和 ‘else’ 區塊已發射,我們可以完成 merge 程式碼
// Emit merge block.
TheFunction->insert(TheFunction->end(), MergeBB);
Builder->SetInsertPoint(MergeBB);
PHINode *PN =
Builder->CreatePHI(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext), 2, "iftmp");
PN->addIncoming(ThenV, ThenBB);
PN->addIncoming(ElseV, ElseBB);
return PN;
}
此處的前兩行現在很熟悉:第一行將 “merge” 區塊添加到 Function 物件(它先前是浮動的,就像上面的 else 區塊一樣)。第二行變更插入點,以便新建立的程式碼將進入 “merge” 區塊。完成此操作後,我們需要建立 PHI 節點並為 PHI 設定區塊/值對。
最後,CodeGen 函數返回 phi 節點作為 if/then/else 表達式計算的值。在我們的範例中,此傳回值將饋送到頂層函數的程式碼中,該程式碼將建立 return 指令。
總之,我們現在有能力在 Kaleidoscope 中執行條件程式碼。透過此擴展,Kaleidoscope 成為一種相當完整的語言,可以計算各種數值函數。接下來,我們將添加另一個有用的表達式,該表達式在非函數式語言中很常見……
5.3. ‘for’ 迴圈表達式¶
現在我們知道如何在語言中添加基本控制流程建構,我們就擁有添加更強大功能的工具。讓我們添加更積極的東西,一個 ‘for’ 表達式
extern putchard(char);
def printstar(n)
for i = 1, i < n, 1.0 in
putchard(42); # ascii 42 = '*'
# print 100 '*' characters
printstar(100);
此表達式定義了一個新的變數(在本例中為 “i”),它從起始值開始迭代,當條件(在本例中為 “i < n”)為 true 時,以可選的步進值(在本例中為 “1.0”)遞增。如果省略步進值,則預設為 1.0。當迴圈為 true 時,它會執行其主體表達式。由於我們沒有更好的東西可以返回,我們只會將迴圈定義為始終返回 0.0。將來當我們有可變變數時,它會變得更有用。
與之前一樣,讓我們討論一下我們需要對 Kaleidoscope 進行的變更,以支援此功能。
5.3.1. ‘for’ 迴圈的詞法分析器擴展¶
詞法分析器擴展與 if/then/else 的類型相同
... in enum Token ...
// control
tok_if = -6, tok_then = -7, tok_else = -8,
tok_for = -9, tok_in = -10
... in gettok ...
if (IdentifierStr == "def")
return tok_def;
if (IdentifierStr == "extern")
return tok_extern;
if (IdentifierStr == "if")
return tok_if;
if (IdentifierStr == "then")
return tok_then;
if (IdentifierStr == "else")
return tok_else;
if (IdentifierStr == "for")
return tok_for;
if (IdentifierStr == "in")
return tok_in;
return tok_identifier;
5.3.2. ‘for’ 迴圈的抽象語法樹擴展¶
抽象語法樹節點同樣簡單。它基本上歸結為捕獲節點中的變數名稱和組成表達式。
/// ForExprAST - Expression class for for/in.
class ForExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::string VarName;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Start, End, Step, Body;
public:
ForExprAST(const std::string &VarName, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Start,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> End, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Step,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Body)
: VarName(VarName), Start(std::move(Start)), End(std::move(End)),
Step(std::move(Step)), Body(std::move(Body)) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
5.3.3. ‘for’ 迴圈的剖析器擴展¶
剖析器程式碼也很標準。這裡唯一有趣的事情是處理可選的步進值。剖析器程式碼透過檢查第二個逗號是否存在來處理它。如果不存在,它會在抽象語法樹節點中將步進值設定為 null
/// forexpr ::= 'for' identifier '=' expr ',' expr (',' expr)? 'in' expression
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseForExpr() {
getNextToken(); // eat the for.
if (CurTok != tok_identifier)
return LogError("expected identifier after for");
std::string IdName = IdentifierStr;
getNextToken(); // eat identifier.
if (CurTok != '=')
return LogError("expected '=' after for");
getNextToken(); // eat '='.
auto Start = ParseExpression();
if (!Start)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != ',')
return LogError("expected ',' after for start value");
getNextToken();
auto End = ParseExpression();
if (!End)
return nullptr;
// The step value is optional.
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Step;
if (CurTok == ',') {
getNextToken();
Step = ParseExpression();
if (!Step)
return nullptr;
}
if (CurTok != tok_in)
return LogError("expected 'in' after for");
getNextToken(); // eat 'in'.
auto Body = ParseExpression();
if (!Body)
return nullptr;
return std::make_unique<ForExprAST>(IdName, std::move(Start),
std::move(End), std::move(Step),
std::move(Body));
}
我們再次將其連接為主要表達式
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (CurTok) {
default:
return LogError("unknown token when expecting an expression");
case tok_identifier:
return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case tok_number:
return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(':
return ParseParenExpr();
case tok_if:
return ParseIfExpr();
case tok_for:
return ParseForExpr();
}
}
5.3.4. ‘for’ 迴圈的 LLVM IR¶
現在我們進入了重點:我們想要為此產生的 LLVM IR。透過上面的簡單範例,我們獲得了這個 LLVM IR(請注意,此轉儲是在停用最佳化的情況下產生的,以提高清晰度)
declare double @putchard(double)
define double @printstar(double %n) {
entry:
; initial value = 1.0 (inlined into phi)
br label %loop
loop: ; preds = %loop, %entry
%i = phi double [ 1.000000e+00, %entry ], [ %nextvar, %loop ]
; body
%calltmp = call double @putchard(double 4.200000e+01)
; increment
%nextvar = fadd double %i, 1.000000e+00
; termination test
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %i, %n
%booltmp = uitofp i1 %cmptmp to double
%loopcond = fcmp one double %booltmp, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %loopcond, label %loop, label %afterloop
afterloop: ; preds = %loop
; loop always returns 0.0
ret double 0.000000e+00
}
此迴圈包含我們之前看到的所有相同建構:phi 節點、多個表達式和一些基本區塊。讓我們看看這是如何組合在一起的。
5.3.5. ‘for’ 迴圈的程式碼產生¶
程式碼產生的第一部分非常簡單:我們只輸出迴圈值的開始表達式
Value *ForExprAST::codegen() {
// Emit the start code first, without 'variable' in scope.
Value *StartVal = Start->codegen();
if (!StartVal)
return nullptr;
完成此操作後,下一步是為迴圈主體的開始設定 LLVM 基本區塊。在上面的情況下,整個迴圈主體是一個區塊,但請記住,主體程式碼本身可能由多個區塊組成(例如,如果它包含 if/then/else 或 for/in 表達式)。
// Make the new basic block for the loop header, inserting after current
// block.
Function *TheFunction = Builder->GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
BasicBlock *PreheaderBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
BasicBlock *LoopBB =
BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "loop", TheFunction);
// Insert an explicit fall through from the current block to the LoopBB.
Builder->CreateBr(LoopBB);
此程式碼與我們在 if/then/else 中看到的程式碼類似。由於我們需要它來建立 Phi 節點,因此我們記住 fall through 到迴圈中的區塊。一旦我們有了它,我們就建立啟動迴圈的實際區塊,並為兩個區塊之間的 fall-through 建立無條件分支。
// Start insertion in LoopBB.
Builder->SetInsertPoint(LoopBB);
// Start the PHI node with an entry for Start.
PHINode *Variable = Builder->CreatePHI(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext),
2, VarName);
Variable->addIncoming(StartVal, PreheaderBB);
現在迴圈的 “preheader” 已設定完成,我們切換到為迴圈主體發射程式碼。首先,我們移動插入點並為迴圈歸納變數建立 PHI 節點。由於我們已經知道起始值的傳入值,因此我們將其添加到 Phi 節點。請注意,Phi 最終將獲得後邊緣的第二個值,但我們還無法設定它(因為它不存在!)。
// Within the loop, the variable is defined equal to the PHI node. If it
// shadows an existing variable, we have to restore it, so save it now.
Value *OldVal = NamedValues[VarName];
NamedValues[VarName] = Variable;
// Emit the body of the loop. This, like any other expr, can change the
// current BB. Note that we ignore the value computed by the body, but don't
// allow an error.
if (!Body->codegen())
return nullptr;
現在程式碼開始變得更有趣了。我們的 ‘for’ 迴圈向符號表引入了一個新變數。這表示我們的符號表現在可以包含函數引數或迴圈變數。為了處理這個問題,在我們產生迴圈主體的程式碼之前,我們將迴圈變數添加為其名稱的目前值。請注意,外部範圍中可能存在同名的變數。將其設為錯誤(如果 VarName 已經有一個條目,則發出錯誤並返回 null)很容易,但我們選擇允許變數遮蔽。為了正確處理這個問題,我們記住我們可能在 OldVal 中遮蔽的 Value(如果沒有遮蔽的變數,則為 null)。
將迴圈變數設定到符號表中後,程式碼會遞迴地產生主體的程式碼。這允許主體使用迴圈變數:對它的任何參考都會自然地在符號表中找到它。
// Emit the step value.
Value *StepVal = nullptr;
if (Step) {
StepVal = Step->codegen();
if (!StepVal)
return nullptr;
} else {
// If not specified, use 1.0.
StepVal = ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(1.0));
}
Value *NextVar = Builder->CreateFAdd(Variable, StepVal, "nextvar");
現在主體已發射,我們透過添加步進值(如果不存在,則為 1.0)來計算迭代變數的下一個值。‘NextVar’ 將是迴圈變數在迴圈的下一次迭代中的值。
// Compute the end condition.
Value *EndCond = End->codegen();
if (!EndCond)
return nullptr;
// Convert condition to a bool by comparing non-equal to 0.0.
EndCond = Builder->CreateFCmpONE(
EndCond, ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(0.0)), "loopcond");
最後,我們評估迴圈的結束值,以確定迴圈是否應該結束。這反映了 if/then/else 陳述句的條件評估。
// Create the "after loop" block and insert it.
BasicBlock *LoopEndBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
BasicBlock *AfterBB =
BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "afterloop", TheFunction);
// Insert the conditional branch into the end of LoopEndBB.
Builder->CreateCondBr(EndCond, LoopBB, AfterBB);
// Any new code will be inserted in AfterBB.
Builder->SetInsertPoint(AfterBB);
隨著迴圈主體的程式碼完成,我們只需要完成其控制流程。此程式碼記住結束區塊(用於 phi 節點),然後建立迴圈結束的區塊(“afterloop”)。根據結束條件的值,它會建立一個條件分支,該分支在再次執行迴圈和結束迴圈之間進行選擇。任何未來的程式碼都在 “afterloop” 區塊中發射,因此它將插入位置設定為它。
// Add a new entry to the PHI node for the backedge.
Variable->addIncoming(NextVar, LoopEndBB);
// Restore the unshadowed variable.
if (OldVal)
NamedValues[VarName] = OldVal;
else
NamedValues.erase(VarName);
// for expr always returns 0.0.
return Constant::getNullValue(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext));
}
最後的程式碼處理各種清理:現在我們有了 “NextVar” 值,我們可以將傳入值添加到迴圈 PHI 節點。之後,我們從符號表中移除迴圈變數,以便在 for 迴圈之後它不在範圍內。最後,for 迴圈的程式碼產生始終返回 0.0,這就是我們從 ForExprAST::codegen() 返回的值。
至此,我們結束了教學的 “向 Kaleidoscope 添加控制流程” 章節。在本章中,我們添加了兩個控制流程建構,並使用它們來激勵 LLVM IR 的幾個方面,這些方面對於前端實作人員來說很重要。在我們傳奇故事的下一章中,我們將變得更加瘋狂,並為我們可憐的無辜語言添加使用者定義的運算符。
5.4. 完整程式碼列表¶
以下是我們正在執行的範例的完整程式碼列表,其中增強了 if/then/else 和 for 表達式。若要建構此範例,請使用
# Compile
clang++ -g toy.cpp `llvm-config --cxxflags --ldflags --system-libs --libs core orcjit native` -O3 -o toy
# Run
./toy
以下是程式碼
#include "../include/KaleidoscopeJIT.h"
#include "llvm/ADT/APFloat.h"
#include "llvm/ADT/STLExtras.h"
#include "llvm/IR/BasicBlock.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Constants.h"
#include "llvm/IR/DerivedTypes.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Function.h"
#include "llvm/IR/IRBuilder.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Instructions.h"
#include "llvm/IR/LLVMContext.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Module.h"
#include "llvm/IR/PassManager.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Type.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Verifier.h"
#include "llvm/Passes/PassBuilder.h"
#include "llvm/Passes/StandardInstrumentations.h"
#include "llvm/Support/TargetSelect.h"
#include "llvm/Target/TargetMachine.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/InstCombine/InstCombine.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/Scalar.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/Scalar/GVN.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/Scalar/Reassociate.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/Scalar/SimplifyCFG.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <map>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace llvm;
using namespace llvm::orc;
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Lexer
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// The lexer returns tokens [0-255] if it is an unknown character, otherwise one
// of these for known things.
enum Token {
tok_eof = -1,
// commands
tok_def = -2,
tok_extern = -3,
// primary
tok_identifier = -4,
tok_number = -5,
// control
tok_if = -6,
tok_then = -7,
tok_else = -8,
tok_for = -9,
tok_in = -10
};
static std::string IdentifierStr; // Filled in if tok_identifier
static double NumVal; // Filled in if tok_number
/// gettok - Return the next token from standard input.
static int gettok() {
static int LastChar = ' ';
// Skip any whitespace.
while (isspace(LastChar))
LastChar = getchar();
if (isalpha(LastChar)) { // identifier: [a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*
IdentifierStr = LastChar;
while (isalnum((LastChar = getchar())))
IdentifierStr += LastChar;
if (IdentifierStr == "def")
return tok_def;
if (IdentifierStr == "extern")
return tok_extern;
if (IdentifierStr == "if")
return tok_if;
if (IdentifierStr == "then")
return tok_then;
if (IdentifierStr == "else")
return tok_else;
if (IdentifierStr == "for")
return tok_for;
if (IdentifierStr == "in")
return tok_in;
return tok_identifier;
}
if (isdigit(LastChar) || LastChar == '.') { // Number: [0-9.]+
std::string NumStr;
do {
NumStr += LastChar;
LastChar = getchar();
} while (isdigit(LastChar) || LastChar == '.');
NumVal = strtod(NumStr.c_str(), nullptr);
return tok_number;
}
if (LastChar == '#') {
// Comment until end of line.
do
LastChar = getchar();
while (LastChar != EOF && LastChar != '\n' && LastChar != '\r');
if (LastChar != EOF)
return gettok();
}
// Check for end of file. Don't eat the EOF.
if (LastChar == EOF)
return tok_eof;
// Otherwise, just return the character as its ascii value.
int ThisChar = LastChar;
LastChar = getchar();
return ThisChar;
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Abstract Syntax Tree (aka Parse Tree)
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
namespace {
/// ExprAST - Base class for all expression nodes.
class ExprAST {
public:
virtual ~ExprAST() = default;
virtual Value *codegen() = 0;
};
/// NumberExprAST - Expression class for numeric literals like "1.0".
class NumberExprAST : public ExprAST {
double Val;
public:
NumberExprAST(double Val) : Val(Val) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
/// VariableExprAST - Expression class for referencing a variable, like "a".
class VariableExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::string Name;
public:
VariableExprAST(const std::string &Name) : Name(Name) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
/// BinaryExprAST - Expression class for a binary operator.
class BinaryExprAST : public ExprAST {
char Op;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LHS, RHS;
public:
BinaryExprAST(char Op, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LHS,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> RHS)
: Op(Op), LHS(std::move(LHS)), RHS(std::move(RHS)) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
/// CallExprAST - Expression class for function calls.
class CallExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::string Callee;
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> Args;
public:
CallExprAST(const std::string &Callee,
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> Args)
: Callee(Callee), Args(std::move(Args)) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
/// IfExprAST - Expression class for if/then/else.
class IfExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Cond, Then, Else;
public:
IfExprAST(std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Cond, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Then,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Else)
: Cond(std::move(Cond)), Then(std::move(Then)), Else(std::move(Else)) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
/// ForExprAST - Expression class for for/in.
class ForExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::string VarName;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Start, End, Step, Body;
public:
ForExprAST(const std::string &VarName, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Start,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> End, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Step,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Body)
: VarName(VarName), Start(std::move(Start)), End(std::move(End)),
Step(std::move(Step)), Body(std::move(Body)) {}
Value *codegen() override;
};
/// PrototypeAST - This class represents the "prototype" for a function,
/// which captures its name, and its argument names (thus implicitly the number
/// of arguments the function takes).
class PrototypeAST {
std::string Name;
std::vector<std::string> Args;
public:
PrototypeAST(const std::string &Name, std::vector<std::string> Args)
: Name(Name), Args(std::move(Args)) {}
Function *codegen();
const std::string &getName() const { return Name; }
};
/// FunctionAST - This class represents a function definition itself.
class FunctionAST {
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> Proto;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Body;
public:
FunctionAST(std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> Proto,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Body)
: Proto(std::move(Proto)), Body(std::move(Body)) {}
Function *codegen();
};
} // end anonymous namespace
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Parser
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
/// CurTok/getNextToken - Provide a simple token buffer. CurTok is the current
/// token the parser is looking at. getNextToken reads another token from the
/// lexer and updates CurTok with its results.
static int CurTok;
static int getNextToken() { return CurTok = gettok(); }
/// BinopPrecedence - This holds the precedence for each binary operator that is
/// defined.
static std::map<char, int> BinopPrecedence;
/// GetTokPrecedence - Get the precedence of the pending binary operator token.
static int GetTokPrecedence() {
if (!isascii(CurTok))
return -1;
// Make sure it's a declared binop.
int TokPrec = BinopPrecedence[CurTok];
if (TokPrec <= 0)
return -1;
return TokPrec;
}
/// LogError* - These are little helper functions for error handling.
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LogError(const char *Str) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", Str);
return nullptr;
}
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> LogErrorP(const char *Str) {
LogError(Str);
return nullptr;
}
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseExpression();
/// numberexpr ::= number
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseNumberExpr() {
auto Result = std::make_unique<NumberExprAST>(NumVal);
getNextToken(); // consume the number
return std::move(Result);
}
/// parenexpr ::= '(' expression ')'
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseParenExpr() {
getNextToken(); // eat (.
auto V = ParseExpression();
if (!V)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != ')')
return LogError("expected ')'");
getNextToken(); // eat ).
return V;
}
/// identifierexpr
/// ::= identifier
/// ::= identifier '(' expression* ')'
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseIdentifierExpr() {
std::string IdName = IdentifierStr;
getNextToken(); // eat identifier.
if (CurTok != '(') // Simple variable ref.
return std::make_unique<VariableExprAST>(IdName);
// Call.
getNextToken(); // eat (
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> Args;
if (CurTok != ')') {
while (true) {
if (auto Arg = ParseExpression())
Args.push_back(std::move(Arg));
else
return nullptr;
if (CurTok == ')')
break;
if (CurTok != ',')
return LogError("Expected ')' or ',' in argument list");
getNextToken();
}
}
// Eat the ')'.
getNextToken();
return std::make_unique<CallExprAST>(IdName, std::move(Args));
}
/// ifexpr ::= 'if' expression 'then' expression 'else' expression
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseIfExpr() {
getNextToken(); // eat the if.
// condition.
auto Cond = ParseExpression();
if (!Cond)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != tok_then)
return LogError("expected then");
getNextToken(); // eat the then
auto Then = ParseExpression();
if (!Then)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != tok_else)
return LogError("expected else");
getNextToken();
auto Else = ParseExpression();
if (!Else)
return nullptr;
return std::make_unique<IfExprAST>(std::move(Cond), std::move(Then),
std::move(Else));
}
/// forexpr ::= 'for' identifier '=' expr ',' expr (',' expr)? 'in' expression
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseForExpr() {
getNextToken(); // eat the for.
if (CurTok != tok_identifier)
return LogError("expected identifier after for");
std::string IdName = IdentifierStr;
getNextToken(); // eat identifier.
if (CurTok != '=')
return LogError("expected '=' after for");
getNextToken(); // eat '='.
auto Start = ParseExpression();
if (!Start)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != ',')
return LogError("expected ',' after for start value");
getNextToken();
auto End = ParseExpression();
if (!End)
return nullptr;
// The step value is optional.
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Step;
if (CurTok == ',') {
getNextToken();
Step = ParseExpression();
if (!Step)
return nullptr;
}
if (CurTok != tok_in)
return LogError("expected 'in' after for");
getNextToken(); // eat 'in'.
auto Body = ParseExpression();
if (!Body)
return nullptr;
return std::make_unique<ForExprAST>(IdName, std::move(Start), std::move(End),
std::move(Step), std::move(Body));
}
/// primary
/// ::= identifierexpr
/// ::= numberexpr
/// ::= parenexpr
/// ::= ifexpr
/// ::= forexpr
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (CurTok) {
default:
return LogError("unknown token when expecting an expression");
case tok_identifier:
return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case tok_number:
return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(':
return ParseParenExpr();
case tok_if:
return ParseIfExpr();
case tok_for:
return ParseForExpr();
}
}
/// binoprhs
/// ::= ('+' primary)*
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseBinOpRHS(int ExprPrec,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LHS) {
// If this is a binop, find its precedence.
while (true) {
int TokPrec = GetTokPrecedence();
// If this is a binop that binds at least as tightly as the current binop,
// consume it, otherwise we are done.
if (TokPrec < ExprPrec)
return LHS;
// Okay, we know this is a binop.
int BinOp = CurTok;
getNextToken(); // eat binop
// Parse the primary expression after the binary operator.
auto RHS = ParsePrimary();
if (!RHS)
return nullptr;
// If BinOp binds less tightly with RHS than the operator after RHS, let
// the pending operator take RHS as its LHS.
int NextPrec = GetTokPrecedence();
if (TokPrec < NextPrec) {
RHS = ParseBinOpRHS(TokPrec + 1, std::move(RHS));
if (!RHS)
return nullptr;
}
// Merge LHS/RHS.
LHS =
std::make_unique<BinaryExprAST>(BinOp, std::move(LHS), std::move(RHS));
}
}
/// expression
/// ::= primary binoprhs
///
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseExpression() {
auto LHS = ParsePrimary();
if (!LHS)
return nullptr;
return ParseBinOpRHS(0, std::move(LHS));
}
/// prototype
/// ::= id '(' id* ')'
static std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParsePrototype() {
if (CurTok != tok_identifier)
return LogErrorP("Expected function name in prototype");
std::string FnName = IdentifierStr;
getNextToken();
if (CurTok != '(')
return LogErrorP("Expected '(' in prototype");
std::vector<std::string> ArgNames;
while (getNextToken() == tok_identifier)
ArgNames.push_back(IdentifierStr);
if (CurTok != ')')
return LogErrorP("Expected ')' in prototype");
// success.
getNextToken(); // eat ')'.
return std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>(FnName, std::move(ArgNames));
}
/// definition ::= 'def' prototype expression
static std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseDefinition() {
getNextToken(); // eat def.
auto Proto = ParsePrototype();
if (!Proto)
return nullptr;
if (auto E = ParseExpression())
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(Proto), std::move(E));
return nullptr;
}
/// toplevelexpr ::= expression
static std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseTopLevelExpr() {
if (auto E = ParseExpression()) {
// Make an anonymous proto.
auto Proto = std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>("__anon_expr",
std::vector<std::string>());
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(Proto), std::move(E));
}
return nullptr;
}
/// external ::= 'extern' prototype
static std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParseExtern() {
getNextToken(); // eat extern.
return ParsePrototype();
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Code Generation
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
static std::unique_ptr<LLVMContext> TheContext;
static std::unique_ptr<Module> TheModule;
static std::unique_ptr<IRBuilder<>> Builder;
static std::map<std::string, Value *> NamedValues;
static std::unique_ptr<KaleidoscopeJIT> TheJIT;
static std::unique_ptr<FunctionPassManager> TheFPM;
static std::unique_ptr<LoopAnalysisManager> TheLAM;
static std::unique_ptr<FunctionAnalysisManager> TheFAM;
static std::unique_ptr<CGSCCAnalysisManager> TheCGAM;
static std::unique_ptr<ModuleAnalysisManager> TheMAM;
static std::unique_ptr<PassInstrumentationCallbacks> ThePIC;
static std::unique_ptr<StandardInstrumentations> TheSI;
static std::map<std::string, std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST>> FunctionProtos;
static ExitOnError ExitOnErr;
Value *LogErrorV(const char *Str) {
LogError(Str);
return nullptr;
}
Function *getFunction(std::string Name) {
// First, see if the function has already been added to the current module.
if (auto *F = TheModule->getFunction(Name))
return F;
// If not, check whether we can codegen the declaration from some existing
// prototype.
auto FI = FunctionProtos.find(Name);
if (FI != FunctionProtos.end())
return FI->second->codegen();
// If no existing prototype exists, return null.
return nullptr;
}
Value *NumberExprAST::codegen() {
return ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(Val));
}
Value *VariableExprAST::codegen() {
// Look this variable up in the function.
Value *V = NamedValues[Name];
if (!V)
return LogErrorV("Unknown variable name");
return V;
}
Value *BinaryExprAST::codegen() {
Value *L = LHS->codegen();
Value *R = RHS->codegen();
if (!L || !R)
return nullptr;
switch (Op) {
case '+':
return Builder->CreateFAdd(L, R, "addtmp");
case '-':
return Builder->CreateFSub(L, R, "subtmp");
case '*':
return Builder->CreateFMul(L, R, "multmp");
case '<':
L = Builder->CreateFCmpULT(L, R, "cmptmp");
// Convert bool 0/1 to double 0.0 or 1.0
return Builder->CreateUIToFP(L, Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext), "booltmp");
default:
return LogErrorV("invalid binary operator");
}
}
Value *CallExprAST::codegen() {
// Look up the name in the global module table.
Function *CalleeF = getFunction(Callee);
if (!CalleeF)
return LogErrorV("Unknown function referenced");
// If argument mismatch error.
if (CalleeF->arg_size() != Args.size())
return LogErrorV("Incorrect # arguments passed");
std::vector<Value *> ArgsV;
for (unsigned i = 0, e = Args.size(); i != e; ++i) {
ArgsV.push_back(Args[i]->codegen());
if (!ArgsV.back())
return nullptr;
}
return Builder->CreateCall(CalleeF, ArgsV, "calltmp");
}
Value *IfExprAST::codegen() {
Value *CondV = Cond->codegen();
if (!CondV)
return nullptr;
// Convert condition to a bool by comparing non-equal to 0.0.
CondV = Builder->CreateFCmpONE(
CondV, ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(0.0)), "ifcond");
Function *TheFunction = Builder->GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
// Create blocks for the then and else cases. Insert the 'then' block at the
// end of the function.
BasicBlock *ThenBB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "then", TheFunction);
BasicBlock *ElseBB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "else");
BasicBlock *MergeBB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "ifcont");
Builder->CreateCondBr(CondV, ThenBB, ElseBB);
// Emit then value.
Builder->SetInsertPoint(ThenBB);
Value *ThenV = Then->codegen();
if (!ThenV)
return nullptr;
Builder->CreateBr(MergeBB);
// Codegen of 'Then' can change the current block, update ThenBB for the PHI.
ThenBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
// Emit else block.
TheFunction->insert(TheFunction->end(), ElseBB);
Builder->SetInsertPoint(ElseBB);
Value *ElseV = Else->codegen();
if (!ElseV)
return nullptr;
Builder->CreateBr(MergeBB);
// Codegen of 'Else' can change the current block, update ElseBB for the PHI.
ElseBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
// Emit merge block.
TheFunction->insert(TheFunction->end(), MergeBB);
Builder->SetInsertPoint(MergeBB);
PHINode *PN = Builder->CreatePHI(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext), 2, "iftmp");
PN->addIncoming(ThenV, ThenBB);
PN->addIncoming(ElseV, ElseBB);
return PN;
}
// Output for-loop as:
// ...
// start = startexpr
// goto loop
// loop:
// variable = phi [start, loopheader], [nextvariable, loopend]
// ...
// bodyexpr
// ...
// loopend:
// step = stepexpr
// nextvariable = variable + step
// endcond = endexpr
// br endcond, loop, endloop
// outloop:
Value *ForExprAST::codegen() {
// Emit the start code first, without 'variable' in scope.
Value *StartVal = Start->codegen();
if (!StartVal)
return nullptr;
// Make the new basic block for the loop header, inserting after current
// block.
Function *TheFunction = Builder->GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
BasicBlock *PreheaderBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
BasicBlock *LoopBB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "loop", TheFunction);
// Insert an explicit fall through from the current block to the LoopBB.
Builder->CreateBr(LoopBB);
// Start insertion in LoopBB.
Builder->SetInsertPoint(LoopBB);
// Start the PHI node with an entry for Start.
PHINode *Variable =
Builder->CreatePHI(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext), 2, VarName);
Variable->addIncoming(StartVal, PreheaderBB);
// Within the loop, the variable is defined equal to the PHI node. If it
// shadows an existing variable, we have to restore it, so save it now.
Value *OldVal = NamedValues[VarName];
NamedValues[VarName] = Variable;
// Emit the body of the loop. This, like any other expr, can change the
// current BB. Note that we ignore the value computed by the body, but don't
// allow an error.
if (!Body->codegen())
return nullptr;
// Emit the step value.
Value *StepVal = nullptr;
if (Step) {
StepVal = Step->codegen();
if (!StepVal)
return nullptr;
} else {
// If not specified, use 1.0.
StepVal = ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(1.0));
}
Value *NextVar = Builder->CreateFAdd(Variable, StepVal, "nextvar");
// Compute the end condition.
Value *EndCond = End->codegen();
if (!EndCond)
return nullptr;
// Convert condition to a bool by comparing non-equal to 0.0.
EndCond = Builder->CreateFCmpONE(
EndCond, ConstantFP::get(*TheContext, APFloat(0.0)), "loopcond");
// Create the "after loop" block and insert it.
BasicBlock *LoopEndBB = Builder->GetInsertBlock();
BasicBlock *AfterBB =
BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "afterloop", TheFunction);
// Insert the conditional branch into the end of LoopEndBB.
Builder->CreateCondBr(EndCond, LoopBB, AfterBB);
// Any new code will be inserted in AfterBB.
Builder->SetInsertPoint(AfterBB);
// Add a new entry to the PHI node for the backedge.
Variable->addIncoming(NextVar, LoopEndBB);
// Restore the unshadowed variable.
if (OldVal)
NamedValues[VarName] = OldVal;
else
NamedValues.erase(VarName);
// for expr always returns 0.0.
return Constant::getNullValue(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext));
}
Function *PrototypeAST::codegen() {
// Make the function type: double(double,double) etc.
std::vector<Type *> Doubles(Args.size(), Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext));
FunctionType *FT =
FunctionType::get(Type::getDoubleTy(*TheContext), Doubles, false);
Function *F =
Function::Create(FT, Function::ExternalLinkage, Name, TheModule.get());
// Set names for all arguments.
unsigned Idx = 0;
for (auto &Arg : F->args())
Arg.setName(Args[Idx++]);
return F;
}
Function *FunctionAST::codegen() {
// Transfer ownership of the prototype to the FunctionProtos map, but keep a
// reference to it for use below.
auto &P = *Proto;
FunctionProtos[Proto->getName()] = std::move(Proto);
Function *TheFunction = getFunction(P.getName());
if (!TheFunction)
return nullptr;
// Create a new basic block to start insertion into.
BasicBlock *BB = BasicBlock::Create(*TheContext, "entry", TheFunction);
Builder->SetInsertPoint(BB);
// Record the function arguments in the NamedValues map.
NamedValues.clear();
for (auto &Arg : TheFunction->args())
NamedValues[std::string(Arg.getName())] = &Arg;
if (Value *RetVal = Body->codegen()) {
// Finish off the function.
Builder->CreateRet(RetVal);
// Validate the generated code, checking for consistency.
verifyFunction(*TheFunction);
// Run the optimizer on the function.
TheFPM->run(*TheFunction, *TheFAM);
return TheFunction;
}
// Error reading body, remove function.
TheFunction->eraseFromParent();
return nullptr;
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Top-Level parsing and JIT Driver
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
static void InitializeModuleAndManagers() {
// Open a new context and module.
TheContext = std::make_unique<LLVMContext>();
TheModule = std::make_unique<Module>("KaleidoscopeJIT", *TheContext);
TheModule->setDataLayout(TheJIT->getDataLayout());
// Create a new builder for the module.
Builder = std::make_unique<IRBuilder<>>(*TheContext);
// Create new pass and analysis managers.
TheFPM = std::make_unique<FunctionPassManager>();
TheLAM = std::make_unique<LoopAnalysisManager>();
TheFAM = std::make_unique<FunctionAnalysisManager>();
TheCGAM = std::make_unique<CGSCCAnalysisManager>();
TheMAM = std::make_unique<ModuleAnalysisManager>();
ThePIC = std::make_unique<PassInstrumentationCallbacks>();
TheSI = std::make_unique<StandardInstrumentations>(*TheContext,
/*DebugLogging*/ true);
TheSI->registerCallbacks(*ThePIC, TheMAM.get());
// Add transform passes.
// Do simple "peephole" optimizations and bit-twiddling optzns.
TheFPM->addPass(InstCombinePass());
// Reassociate expressions.
TheFPM->addPass(ReassociatePass());
// Eliminate Common SubExpressions.
TheFPM->addPass(GVNPass());
// Simplify the control flow graph (deleting unreachable blocks, etc).
TheFPM->addPass(SimplifyCFGPass());
// Register analysis passes used in these transform passes.
PassBuilder PB;
PB.registerModuleAnalyses(*TheMAM);
PB.registerFunctionAnalyses(*TheFAM);
PB.crossRegisterProxies(*TheLAM, *TheFAM, *TheCGAM, *TheMAM);
}
static void HandleDefinition() {
if (auto FnAST = ParseDefinition()) {
if (auto *FnIR = FnAST->codegen()) {
fprintf(stderr, "Read function definition:");
FnIR->print(errs());
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
ExitOnErr(TheJIT->addModule(
ThreadSafeModule(std::move(TheModule), std::move(TheContext))));
InitializeModuleAndManagers();
}
} else {
// Skip token for error recovery.
getNextToken();
}
}
static void HandleExtern() {
if (auto ProtoAST = ParseExtern()) {
if (auto *FnIR = ProtoAST->codegen()) {
fprintf(stderr, "Read extern: ");
FnIR->print(errs());
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
FunctionProtos[ProtoAST->getName()] = std::move(ProtoAST);
}
} else {
// Skip token for error recovery.
getNextToken();
}
}
static void HandleTopLevelExpression() {
// Evaluate a top-level expression into an anonymous function.
if (auto FnAST = ParseTopLevelExpr()) {
if (FnAST->codegen()) {
// Create a ResourceTracker to track JIT'd memory allocated to our
// anonymous expression -- that way we can free it after executing.
auto RT = TheJIT->getMainJITDylib().createResourceTracker();
auto TSM = ThreadSafeModule(std::move(TheModule), std::move(TheContext));
ExitOnErr(TheJIT->addModule(std::move(TSM), RT));
InitializeModuleAndManagers();
// Search the JIT for the __anon_expr symbol.
auto ExprSymbol = ExitOnErr(TheJIT->lookup("__anon_expr"));
// Get the symbol's address and cast it to the right type (takes no
// arguments, returns a double) so we can call it as a native function.
double (*FP)() = ExprSymbol.toPtr<double (*)()>();
fprintf(stderr, "Evaluated to %f\n", FP());
// Delete the anonymous expression module from the JIT.
ExitOnErr(RT->remove());
}
} else {
// Skip token for error recovery.
getNextToken();
}
}
/// top ::= definition | external | expression | ';'
static void MainLoop() {
while (true) {
fprintf(stderr, "ready> ");
switch (CurTok) {
case tok_eof:
return;
case ';': // ignore top-level semicolons.
getNextToken();
break;
case tok_def:
HandleDefinition();
break;
case tok_extern:
HandleExtern();
break;
default:
HandleTopLevelExpression();
break;
}
}
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// "Library" functions that can be "extern'd" from user code.
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
#ifdef _WIN32
#define DLLEXPORT __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define DLLEXPORT
#endif
/// putchard - putchar that takes a double and returns 0.
extern "C" DLLEXPORT double putchard(double X) {
fputc((char)X, stderr);
return 0;
}
/// printd - printf that takes a double prints it as "%f\n", returning 0.
extern "C" DLLEXPORT double printd(double X) {
fprintf(stderr, "%f\n", X);
return 0;
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Main driver code.
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
int main() {
InitializeNativeTarget();
InitializeNativeTargetAsmPrinter();
InitializeNativeTargetAsmParser();
// Install standard binary operators.
// 1 is lowest precedence.
BinopPrecedence['<'] = 10;
BinopPrecedence['+'] = 20;
BinopPrecedence['-'] = 20;
BinopPrecedence['*'] = 40; // highest.
// Prime the first token.
fprintf(stderr, "ready> ");
getNextToken();
TheJIT = ExitOnErr(KaleidoscopeJIT::Create());
InitializeModuleAndManagers();
// Run the main "interpreter loop" now.
MainLoop();
return 0;
}
